Enterprise Software Tools: 7 Powerful Solutions to Transform Your Business
In today’s fast-paced digital world, enterprise software tools are no longer optional—they’re essential. From streamlining operations to boosting collaboration, the right tools can revolutionize how your organization works. Let’s dive into the most powerful solutions shaping modern enterprises.
1. Understanding Enterprise Software Tools: Definition and Core Purpose

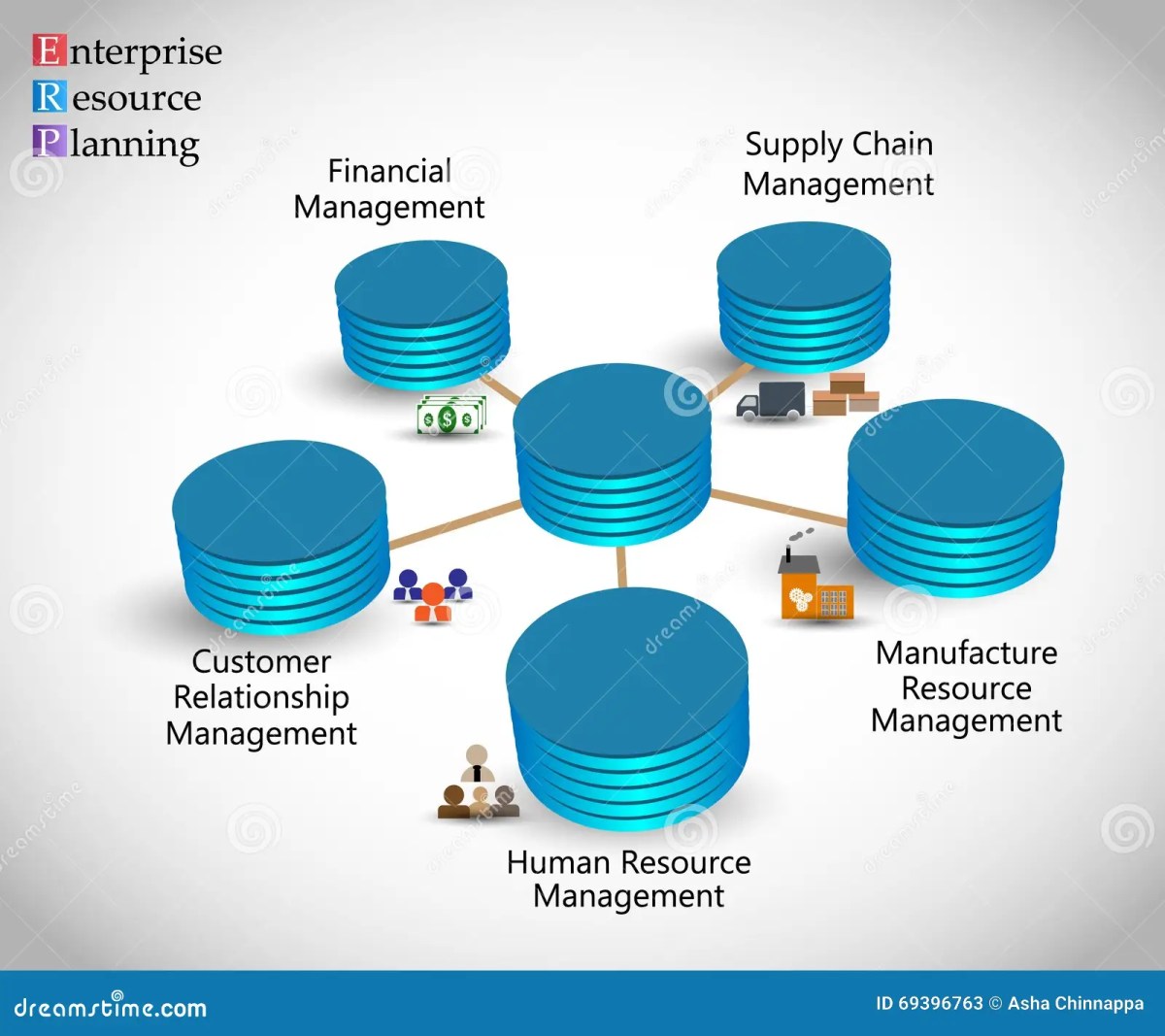
Enterprise software tools are comprehensive digital systems designed to support large-scale business operations. Unlike consumer-grade applications, these tools are built for scalability, security, and integration across departments such as finance, HR, sales, and IT. They serve as the backbone of modern organizations, enabling data-driven decisions and operational efficiency.
What Qualifies as Enterprise-Grade Software?
Enterprise software is distinguished by several key characteristics that set it apart from standard business applications. These include robust security protocols, multi-user support, high availability, and the ability to integrate with other enterprise systems. These tools are typically deployed across multiple departments and often support thousands of users simultaneously.
- Scalability: Can grow with the organization, supporting increased data loads and user counts.
- Security: Offers advanced access controls, encryption, and compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
- Integration: Seamlessly connects with existing systems via APIs and middleware.
Common Use Cases Across Industries
Enterprise software tools are not limited to tech companies. They are widely used across sectors including healthcare, manufacturing, finance, retail, and government. For example, hospitals use enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems to manage patient records and supply chains, while manufacturers rely on them for production scheduling and inventory control.
- Financial institutions use enterprise software for risk management and regulatory reporting.
- Retailers leverage customer relationship management (CRM) tools to personalize marketing and improve service.
- Logistics companies use supply chain management (SCM) platforms to track shipments in real time.
“Enterprise software is the central nervous system of a modern organization.” — Gartner Research
2. Top 7 Enterprise Software Tools Revolutionizing Business Operations
The market is flooded with enterprise software tools, but only a few deliver transformative results. Below are seven of the most impactful solutions that leading organizations rely on to stay competitive, efficient, and agile in a digital-first world.
1. SAP S/4HANA: The Intelligent ERP Platform
SAP S/4HANA is a next-generation ERP suite that leverages in-memory computing to deliver real-time analytics and process automation. It’s designed for large enterprises seeking to unify finance, logistics, manufacturing, and supply chain operations under one intelligent platform.
- Offers AI-powered forecasting and predictive analytics.
- Supports cloud, on-premise, and hybrid deployment models.
- Integrates with SAP’s ecosystem of industry-specific solutions.
According to SAP’s official site, over 14,000 customers globally use S/4HANA to drive digital transformation. Learn more about SAP S/4HANA.
2. Oracle Fusion Cloud ERP
Oracle Fusion Cloud ERP is a comprehensive suite that combines financial management, procurement, project management, and risk compliance into a single cloud-based platform. It’s known for its deep analytics, machine learning capabilities, and global compliance support.
- Automates financial close processes and improves reporting accuracy.
- Provides real-time insights into cash flow and budget performance.
- Offers built-in AI for fraud detection and anomaly identification.
Oracle’s cloud ERP is used by Fortune 500 companies like Nissan and Schlumberger. Explore Oracle ERP.
3. Microsoft Dynamics 365
Microsoft Dynamics 365 is a modular suite that blends ERP and CRM functionalities. It integrates seamlessly with Microsoft 365, Power BI, and Azure, making it ideal for organizations already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem.
- Modules include Finance, Supply Chain Management, Sales, Customer Service, and Field Service.
- Leverages AI for sales forecasting and customer sentiment analysis.
- Offers low-code customization through Power Apps.
Dynamics 365 is used by companies like Toyota and Heineken. Visit Microsoft Dynamics 365.
4. Salesforce Customer 360
Salesforce is the world leader in CRM, and its Customer 360 platform enables enterprises to create a unified view of every customer across sales, service, marketing, and commerce.
- Uses Einstein AI to recommend next-best actions for sales reps.
- Supports omnichannel customer engagement (email, chat, social media).
- Integrates with external systems via MuleSoft, Salesforce’s integration platform.
Salesforce powers customer experiences for companies like Amazon Web Services and Spotify. Discover Salesforce Platform.
5. ServiceNow IT Service Management (ITSM)
ServiceNow is a leader in digital workflow automation, particularly in IT service management. Its platform helps enterprises streamline incident resolution, change management, and IT operations.
- Offers a centralized service portal for employees and IT teams.
- Uses AI for intelligent ticket routing and root cause analysis.
- Extends beyond IT to HR, security, and customer workflows.
ServiceNow is trusted by 70% of the Fortune 500. Learn about ServiceNow ITSM.
6. Workday Human Capital Management (HCM)
Workday HCM is a cloud-based solution for managing workforce planning, payroll, talent development, and employee experience. It’s especially popular in large, global organizations.
- Provides real-time workforce analytics and succession planning.
- Supports global payroll compliance across 130+ countries.
- Offers mobile-first design for employee self-service.
Workday serves clients like Netflix and Toyota. Explore Workday HCM.
7. Adobe Experience Cloud
For enterprises focused on digital marketing and customer experience, Adobe Experience Cloud offers a powerful suite of tools for content management, personalization, analytics, and advertising.
- Enables real-time personalization across websites, apps, and emails.
- Integrates with CRM and ERP systems for unified customer data.
- Uses AI (Adobe Sensei) for content recommendations and predictive insights.
Brands like IBM and Marriott use Adobe Experience Cloud to deliver engaging digital experiences. Visit Adobe Experience Cloud.
3. Key Benefits of Implementing Enterprise Software Tools
Deploying enterprise software tools isn’t just about replacing old systems—it’s about unlocking new levels of performance, visibility, and agility. The benefits extend far beyond automation, touching every aspect of organizational health.
Improved Operational Efficiency
One of the most immediate impacts of enterprise software is the reduction of manual work. By automating repetitive tasks like data entry, invoice processing, and report generation, these tools free up employees to focus on higher-value activities.
- Reduces processing time by up to 70% in finance and HR departments.
- Minimizes human error in critical operations.
- Enables faster decision-making through real-time dashboards.
Enhanced Data Visibility and Analytics
Enterprise software tools consolidate data from disparate sources into a single source of truth. This unified data model allows leaders to gain insights that were previously hidden in siloed systems.
- Provides real-time KPIs across departments.
- Supports predictive analytics for demand forecasting and risk assessment.
- Enables self-service reporting through tools like Power BI and Tableau integrations.
Scalability and Future-Proofing
As businesses grow, their software must grow with them. Enterprise tools are designed to scale horizontally and vertically, supporting new users, locations, and business units without performance degradation.
- Cloud-based platforms allow instant scaling during peak periods.
- Modular architectures let companies add functionality as needed.
- Supports mergers and acquisitions by integrating new entities quickly.
“Companies that invest in enterprise software see 30% faster growth in operational efficiency.” — McKinsey & Company
4. Challenges in Adopting Enterprise Software Tools
Despite their benefits, implementing enterprise software tools is not without hurdles. Organizations often face technical, cultural, and financial challenges that can delay or derail adoption.
High Implementation Costs
Enterprise software often requires significant upfront investment in licensing, infrastructure, consulting, and training. Cloud solutions have reduced some of these costs, but total cost of ownership (TCO) can still be substantial over time.
- Licensing fees can run into millions for large deployments.
- Customization and integration services add to the budget.
- Ongoing maintenance and upgrade costs must be factored in.
Complex Integration with Legacy Systems
Many enterprises still rely on legacy systems that were built decades ago. Integrating modern software with these systems can be technically challenging and risky.
- Data migration often uncovers inconsistencies and quality issues.
- API limitations in older systems hinder real-time connectivity.
- Requires middleware or custom connectors, increasing complexity.
User Resistance and Change Management
Even the best software fails if employees resist using it. Change management is often the most underestimated aspect of enterprise software adoption.
- Employees may fear job displacement or increased workload.
- Lack of training leads to low adoption rates.
- Without executive sponsorship, initiatives lose momentum.
5. How to Choose the Right Enterprise Software Tools for Your Organization
Selecting the right enterprise software is a strategic decision that requires careful evaluation. A one-size-fits-all approach doesn’t work—what works for a multinational may not suit a mid-sized firm.
Assess Your Business Needs and Goals
Start by identifying your core pain points and strategic objectives. Are you looking to improve customer service? Streamline supply chain operations? Enhance financial reporting?
- Conduct stakeholder interviews across departments.
- Map current processes to identify inefficiencies.
- Define measurable goals (e.g., reduce invoice processing time by 50%).
Evaluate Scalability and Flexibility
Choose software that can grow with your business. Look for modular platforms that allow you to start small and expand functionality over time.
- Ensure the platform supports multi-currency, multi-language, and global compliance.
- Check if it offers both cloud and on-premise options.
- Verify API availability for future integrations.
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Look beyond the initial price tag. Calculate long-term costs including licensing, support, training, upgrades, and potential downtime.
- Compare subscription vs. perpetual licensing models.
- Factor in internal IT resource requirements.
- Request detailed pricing from vendors, including volume discounts.
6. The Role of AI and Automation in Modern Enterprise Software Tools
Artificial intelligence and automation are no longer futuristic concepts—they’re embedded in today’s enterprise software tools, driving smarter decisions and reducing manual effort.
AI-Powered Analytics and Predictive Insights
Modern enterprise tools use AI to analyze vast datasets and predict future trends. For example, ERP systems can forecast inventory needs based on historical sales and market conditions.
- Salesforce Einstein predicts customer churn and recommends retention strategies.
- Oracle ERP uses machine learning to detect financial anomalies.
- SAP S/4HANA applies AI to optimize production schedules.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA tools like UiPath and Automation Anywhere are being integrated into enterprise platforms to automate repetitive tasks such as data entry, report generation, and invoice processing.
- Reduces processing time from hours to minutes.
- Operates 24/7 without errors or fatigue.
- Can be deployed alongside existing software without major changes.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Chatbots
NLP enables enterprise software to understand and respond to human language. This powers virtual assistants and chatbots that support employees and customers.
- ServiceNow’s virtual agent handles IT support tickets via chat.
- Workday’s conversational AI helps employees find HR information.
- Microsoft Power Virtual Agents allows non-developers to build bots.
“By 2025, 70% of enterprise software interactions will be driven by AI.” — Gartner
7. Future Trends Shaping Enterprise Software Tools
The enterprise software landscape is evolving rapidly. Emerging technologies and shifting business models are redefining what these tools can do and how they are delivered.
Cloud-Native and Microservices Architecture
Modern enterprise software is increasingly built on cloud-native principles, using microservices and containers for greater agility and resilience.
- Enables faster updates and easier scaling.
- Improves fault isolation—failure in one module doesn’t crash the system.
- Supports DevOps practices for continuous delivery.
Low-Code and No-Code Development
Enterprises are adopting low-code platforms to empower business users to build custom applications without coding expertise.
- Microsoft Power Apps and Salesforce Lightning allow rapid app development.
- Reduces dependency on IT teams for minor changes.
- Speeds up innovation and process customization.
Hyperautomation and Composable Business
Gartner’s concept of hyperautomation involves combining AI, RPA, and process mining to automate entire business functions. Composable business refers to modular, adaptable systems that can be reconfigured quickly.
- Enterprises can assemble software components like building blocks.
- Enables rapid response to market changes.
- Supports innovation through experimentation.
What are enterprise software tools?
Enterprise software tools are large-scale applications designed to support complex business processes across departments like finance, HR, supply chain, and IT. They are built for scalability, security, and integration, serving organizations with hundreds or thousands of users.
What are the most popular enterprise software tools?
Some of the most widely used enterprise software tools include SAP S/4HANA, Oracle Fusion Cloud ERP, Microsoft Dynamics 365, Salesforce Customer 360, ServiceNow ITSM, Workday HCM, and Adobe Experience Cloud. Each serves different functional areas but shares a focus on integration, automation, and analytics.
How do enterprise software tools improve efficiency?
These tools automate manual processes, reduce errors, provide real-time data insights, and enable better collaboration across teams. By centralizing data and streamlining workflows, they help organizations operate faster and with greater accuracy.
What challenges do companies face when implementing enterprise software?
Common challenges include high costs, integration with legacy systems, data migration issues, user resistance, and the need for extensive training. Successful implementation requires strong project management, executive support, and a clear change management strategy.
How is AI transforming enterprise software tools?
AI is enhancing enterprise software with predictive analytics, intelligent automation, natural language processing, and self-learning systems. It enables features like automated customer service, fraud detection, demand forecasting, and personalized employee experiences.
Enterprise software tools are no longer just support systems—they are strategic assets that drive innovation, efficiency, and competitive advantage. From ERP and CRM to AI-powered automation, the right tools can transform how organizations operate. While challenges like cost and integration exist, the long-term benefits far outweigh the risks. As technology evolves, embracing cloud-native, modular, and intelligent platforms will be key to future success. The future of enterprise software is not just about doing things faster—it’s about doing smarter, more adaptive, and more human-centered business.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: