Enterprise Project Management: 7 Powerful Strategies for Success
Navigating the complex world of enterprise project management can feel overwhelming—until you have the right strategies in place. Discover how top organizations streamline workflows, boost collaboration, and deliver results at scale.
What Is Enterprise Project Management?

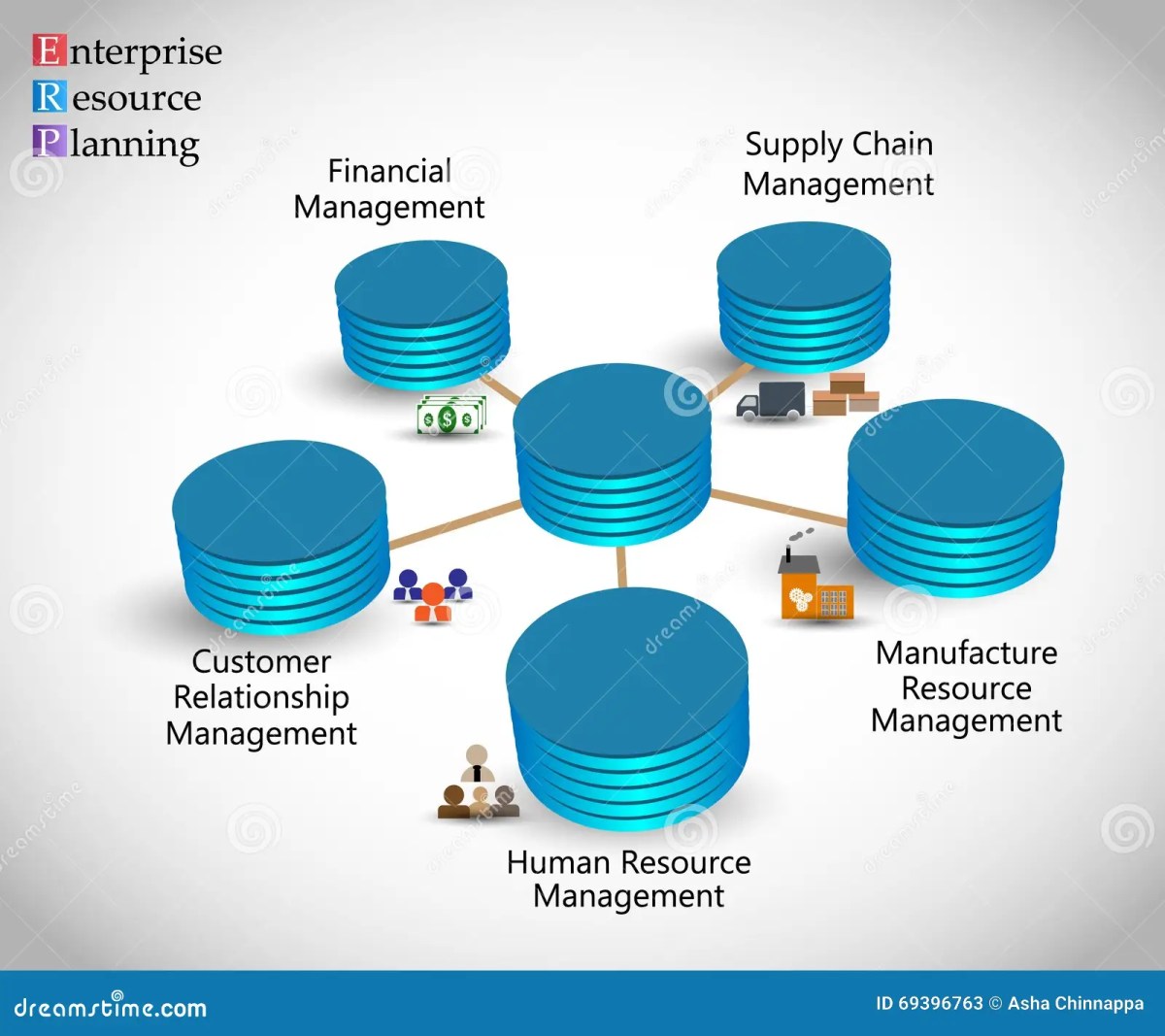
Enterprise project management (EPM) refers to the centralized management of multiple projects across an organization to align with strategic goals. Unlike traditional project management, which focuses on individual initiatives, EPM takes a holistic view, integrating people, processes, and technology across departments and geographies.
Defining the Scope of EPM
The scope of enterprise project management extends beyond timelines and budgets. It encompasses governance, resource allocation, risk management, and performance tracking at an organizational level. This broader perspective ensures that every project contributes to long-term business objectives.
- Manages interdependent projects across departments
- Aligns project outcomes with corporate strategy
- Standardizes processes for consistency and compliance
Key Differences Between EPM and Traditional Project Management
While traditional project management focuses on delivering a single project on time and within budget, enterprise project management operates at a strategic level. It emphasizes portfolio optimization, enterprise-wide resource planning, and executive oversight.
- Traditional PM: Tactical, short-term, team-focused
- EPM: Strategic, long-term, organization-wide
- EPM includes portfolio, program, and project management (P3M)
“Enterprise project management is not just about managing more projects—it’s about managing the right projects the right way.” — PMI, Project Management Institute
The Core Components of Enterprise Project Management
A successful enterprise project management framework relies on several interconnected components. These elements work together to create a scalable, repeatable system for managing complex initiatives.
Project Portfolio Management (PPM)
At the heart of EPM is Project Portfolio Management (PPM), which involves selecting, prioritizing, and overseeing a collection of projects that align with business strategy. PPM enables leadership to make data-driven decisions about where to invest resources.
- Uses scoring models to evaluate project value vs. risk
- Enables dynamic reprioritization based on market changes
- Integrates financial forecasting and capacity planning
Standardized Methodologies and Frameworks
Organizations implementing EPM adopt standardized methodologies such as PMBOK, PRINCE2, or Agile at scale (SAFe). These frameworks provide structure, reduce ambiguity, and ensure consistency across teams.
- PMBOK offers a process-based approach ideal for predictive projects
- SAFe supports Agile transformation in large enterprises
- Hybrid models combine waterfall and Agile for flexibility
Centralized Governance and Oversight
Effective EPM requires a governance structure—often a Project Management Office (PMO)—to set policies, monitor performance, and ensure compliance. This oversight body acts as the steward of project standards and best practices.
- Establishes project approval and review processes
- Conducts regular portfolio health checks
- Provides training and mentorship to project managers
Benefits of Enterprise Project Management
Implementing enterprise project management brings transformative benefits to organizations of all sizes. From improved visibility to enhanced decision-making, EPM creates a foundation for sustainable growth.
Improved Strategic Alignment
One of the most significant advantages of enterprise project management is the ability to align every project with the company’s strategic vision. This ensures that resources are invested in initiatives that drive real business value.
- Links project KPIs to organizational goals
- Reduces duplication of effort across departments
- Enables faster response to market opportunities
Enhanced Resource Optimization
EPM provides a comprehensive view of resource availability and utilization across all projects. This visibility allows for smarter allocation, reducing bottlenecks and preventing overcommitment.
- Tracks skills, availability, and workload in real time
- Supports cross-functional team assignments
- Reduces idle time and improves productivity
Greater Risk Management and Compliance
With enterprise project management, risks are identified, assessed, and mitigated at scale. Standardized risk registers, audit trails, and compliance protocols help organizations meet regulatory requirements and avoid costly setbacks.
- Centralizes risk data for enterprise-wide analysis
- Enables proactive mitigation planning
- Supports ISO, GDPR, SOX, and other compliance standards
“Companies using EPM report 30% fewer project failures due to improved risk visibility.” — Gartner Research
Challenges in Enterprise Project Management
Despite its benefits, enterprise project management is not without challenges. Scaling project practices across large organizations introduces complexity that must be carefully managed.
Organizational Resistance to Change
One of the biggest hurdles in implementing EPM is cultural resistance. Employees and managers accustomed to autonomy may resist standardized processes and centralized oversight.
- Perceived loss of control over project decisions
- Lack of understanding about EPM benefits
- Departmental silos hinder collaboration
Tool Integration and Data Silos
Many organizations use multiple project management tools across departments, leading to fragmented data and inconsistent reporting. Integrating these systems into a unified EPM platform is technically and operationally challenging.
- Legacy systems resist API integration
- Data formats vary across tools
- Real-time synchronization is difficult to achieve
Scaling Agile and Flexibility Constraints
While Agile works well for small teams, scaling it across an enterprise through frameworks like SAFe or LeSS requires significant investment in training and process redesign. Balancing agility with governance remains a key challenge.
- Agile ceremonies become cumbersome at scale
- Compliance requirements slow down iteration cycles
- Hybrid models require careful coordination
Enterprise Project Management Tools and Technologies
The right technology stack is critical for successful enterprise project management. Modern EPM platforms offer robust features for planning, tracking, collaboration, and analytics.
Top EPM Software Solutions
Several enterprise-grade tools dominate the market, each offering unique strengths depending on organizational needs.
- Microsoft Project & Project Online: Ideal for organizations already in the Microsoft ecosystem, offering deep integration with Teams, SharePoint, and Power BI.
- Oracle Primavera P6: A powerhouse for capital-intensive industries like construction and energy, known for its advanced scheduling and resource management.
- Smartsheet: Combines spreadsheet familiarity with enterprise features like dashboards, workflows, and API access.
- Planview: Offers end-to-end PPM capabilities with strong portfolio analytics and strategic planning tools.
- Wrike Enterprise: Supports hybrid methodologies with real-time collaboration and workload management.
Choosing the right tool depends on factors like industry, team size, methodology preference, and integration requirements.
Key Features to Look for in EPM Tools
When evaluating enterprise project management software, organizations should prioritize features that support scalability, visibility, and control.
- Portfolio Dashboards: Visual overviews of project health, resource allocation, and financials.
- Resource Management: Real-time tracking of availability, skills, and workload.
- Workflow Automation: Streamlines approvals, status updates, and reporting.
- Custom Reporting and BI Integration: Enables data-driven decision-making with exportable reports and integration with tools like Tableau or Power BI.
- Security and Compliance: Role-based access, audit logs, and data encryption for enterprise-grade security.
The Role of AI and Automation in EPM
Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning are transforming enterprise project management. AI-powered tools can predict delays, recommend resource allocations, and automate routine tasks.
- Predictive analytics forecast project risks based on historical data
- NLP-powered assistants help with status reporting and meeting summaries
- Automated scheduling adjusts timelines based on team availability
“By 2025, 50% of large enterprises will use AI-driven project insights to improve delivery success rates.” — Forrester
Building a Successful Enterprise Project Management Office (EPMO)
The Enterprise Project Management Office (EPMO) is the engine that drives EPM adoption and maturity. It’s responsible for setting standards, providing support, and ensuring alignment across the organization.
Functions of an EPMO
An effective EPMO performs several critical roles that go beyond administrative support.
- Develops and maintains project management standards and templates
- Provides training and certification programs for project managers
- Monitors project performance and reports to executive leadership
- Facilitates lessons learned and continuous improvement
- Acts as a center of excellence for best practices
Types of EPMOs
Not all EPMOs are the same. Their structure and authority vary based on organizational needs.
- Supportive EPMO: Offers guidance and resources but has no enforcement power.
- Controlling EPMO: Sets standards and conducts audits to ensure compliance.
- Directive EPMO: Directly manages projects and assigns project managers.
Most organizations start with a supportive model and evolve toward controlling or directive as maturity increases.
Measuring EPMO Success
To justify its existence, an EPMO must demonstrate value through measurable outcomes.
- Percentage of projects delivered on time and within budget
- Reduction in project cycle time
- Improvement in stakeholder satisfaction scores
- Increased portfolio ROI
- Adoption rate of EPM tools and processes
Best Practices for Implementing Enterprise Project Management
Rolling out EPM across an organization requires careful planning, leadership buy-in, and a phased approach. These best practices can help ensure a smooth transition.
Secure Executive Sponsorship
Without support from the C-suite, EPM initiatives often fail. Executives must champion the change, allocate budget, and model desired behaviors.
- Assign a senior leader as EPM sponsor
- Align EPM goals with corporate strategy
- Include EPM metrics in executive dashboards
Start with a Pilot Program
Begin with a small group of high-impact projects to test processes and tools. Use lessons learned to refine the approach before scaling.
- Select projects with clear success criteria
- Involve cross-functional teams
- Collect feedback and iterate quickly
Invest in Training and Change Management
People are at the heart of EPM success. Provide comprehensive training and ongoing support to help teams adapt.
- Offer role-based training (e.g., for PMs, team members, sponsors)
- Use internal champions to drive adoption
- Communicate benefits regularly through newsletters and town halls
Establish Clear Metrics and KPIs
Define what success looks like with measurable KPIs. Track progress consistently to demonstrate value and identify areas for improvement.
- On-time delivery rate
- Budget variance
- Resource utilization rate
- Project ROI
- Stakeholder satisfaction (via surveys)
Future Trends in Enterprise Project Management
The field of enterprise project management is evolving rapidly. New technologies, methodologies, and workforce dynamics are shaping the future of how organizations manage complex initiatives.
Rise of Hybrid and Adaptive Methodologies
Organizations are moving away from rigid frameworks toward hybrid models that blend Agile, waterfall, and Lean principles. This flexibility allows teams to adapt to changing requirements without sacrificing governance.
- Agile for software development, waterfall for regulatory projects
- Dynamic methodology switching based on project phase
- Increased use of DevOps and CI/CD pipelines in EPM
Remote and Distributed Teams
The shift to remote work has made collaboration tools and virtual project management essential. EPM systems must support asynchronous communication, time zone awareness, and digital transparency.
- Cloud-based EPM platforms enable global access
- Virtual PMOs coordinate distributed teams
- Digital dashboards replace physical war rooms
Sustainability and ESG Integration
Enterprise project management is increasingly incorporating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria into project selection and evaluation.
- Projects assessed for carbon footprint and social impact
- Sustainability KPIs added to portfolio dashboards
- Green project management practices promoted
What is the difference between project management and enterprise project management?
Traditional project management focuses on delivering a single project on time and within budget, using tools like Gantt charts and task lists. Enterprise project management, on the other hand, manages multiple interrelated projects across an organization, aligning them with strategic goals through centralized governance, portfolio management, and standardized processes.
What role does a PMO play in enterprise project management?
The Project Management Office (PMO) or EPMO serves as the central hub for enterprise project management. It establishes standards, provides tools and training, monitors performance, and ensures projects align with business strategy. It also facilitates communication between project teams and executive leadership.
How do you measure the success of enterprise project management?
Success is measured through KPIs such as project delivery rate, budget adherence, resource utilization, stakeholder satisfaction, and portfolio ROI. Additionally, qualitative factors like improved decision-making and faster time-to-market are important indicators.
What are the best tools for enterprise project management?
Top tools include Microsoft Project, Oracle Primavera P6, Smartsheet, Planview, and Wrike Enterprise. The best choice depends on your industry, team size, methodology, and integration needs.
Can Agile be used in enterprise project management?
Yes, Agile can be scaled for enterprise use through frameworks like SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework), LeSS (Large-Scale Scrum), and Nexus. These models maintain Agile principles while adding structure for coordination, governance, and alignment across large teams.
Enterprise project management is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity for organizations aiming to thrive in a complex, fast-paced world. By adopting a structured approach, leveraging the right tools, and fostering a culture of collaboration and accountability, companies can turn their project portfolios into powerful engines of strategic growth. The journey may be challenging, but the rewards—greater efficiency, improved outcomes, and stronger alignment—are well worth the effort.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: