Enterprise Business Software: 7 Powerful Solutions for 2024
In today’s fast-paced digital world, enterprise business software is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity. From streamlining operations to boosting collaboration, the right tools can transform how large organizations function.
What Is Enterprise Business Software?

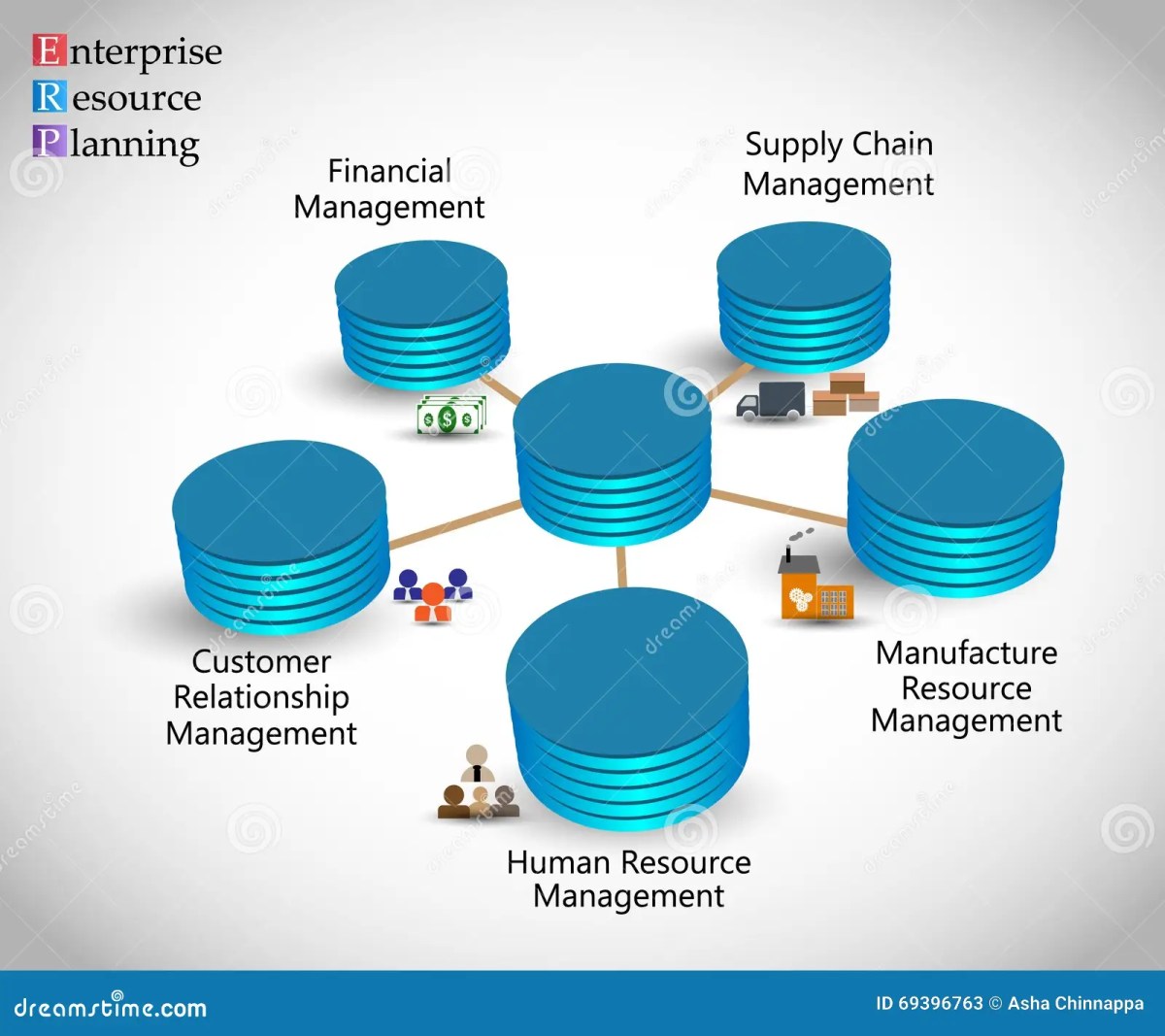
Enterprise business software refers to large-scale software solutions designed to support complex business processes across departments in medium to large organizations. Unlike consumer-grade tools, these systems are built for scalability, security, integration, and high-volume data processing. They serve as the backbone of modern enterprises, enabling seamless coordination between finance, HR, supply chain, sales, and customer service.
Core Characteristics of Enterprise Software
What sets enterprise business software apart from standard applications? It’s not just about size—it’s about capability, reliability, and integration. These systems are engineered to meet the demands of global organizations with thousands of users and terabytes of data.
Scalability: The software must grow with the company, supporting increased users, transactions, and data without performance loss.Integration: It should seamlessly connect with existing systems like CRM, ERP, and HRIS through APIs and middleware.Security: With sensitive corporate data at stake, enterprise software includes advanced encryption, role-based access control, and compliance features (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).Customizability: Businesses have unique workflows.Enterprise software allows configuration and customization to match specific operational needs.Support & Maintenance: Vendors provide 24/7 technical support, regular updates, and service-level agreements (SLAs).”Enterprise software isn’t just about automation—it’s about transformation..
It redefines how organizations operate at scale.” — Gartner Research, 2023Common Types of Enterprise Business SoftwareEnterprise business software isn’t a single product but a suite of interconnected systems.Each serves a distinct function while contributing to overall organizational efficiency..
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning): Integrates core business functions like finance, procurement, and inventory management.Examples include SAP S/4HANA and Oracle ERP Cloud.CRM (Customer Relationship Management): Manages customer interactions, sales pipelines, and marketing campaigns.Salesforce and HubSpot are leading platforms.SCM (Supply Chain Management): Optimizes logistics, procurement, and distribution..
Tools like Kinaxis RapidResponse help manage complex supply networks.HRMS (Human Resource Management Systems): Handles payroll, recruitment, performance reviews, and employee engagement.Workday and Oracle HCM are top contenders.BI (Business Intelligence) & Analytics: Turns raw data into actionable insights.Microsoft Power BI and Tableau are widely used.Collaboration & Productivity Suites: Platforms like Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace enable real-time teamwork across geographies.These systems often work together in an integrated ecosystem, reducing data silos and improving decision-making..
Top 7 Enterprise Business Software Solutions in 2024
The market for enterprise business software is vast and constantly evolving. To help you navigate the options, we’ve curated the seven most powerful and widely adopted solutions in 2024—each offering unique strengths for different business needs.
1. SAP S/4HANA – The Gold Standard in ERP
SAP S/4HANA remains the most dominant ERP system for large enterprises. Built on an in-memory database (HANA), it delivers real-time data processing and analytics, making it ideal for global organizations with complex operations.
- Real-time financial reporting and forecasting
- AI-powered automation for procurement and logistics
- Cloud and on-premise deployment options
- Strong integration with third-party systems via SAP Cloud Platform
SAP’s ecosystem is vast, with over 400,000 customers worldwide. Its industry-specific modules for manufacturing, retail, and healthcare make it highly adaptable. For more information, visit SAP’s official S/4HANA page.
2. Oracle ERP Cloud – Scalable & Secure
Oracle ERP Cloud is a cloud-native solution that excels in financial management, project accounting, and risk compliance. It’s particularly popular among regulated industries like finance and pharmaceuticals.
- Advanced AI for fraud detection and anomaly monitoring
- Automated financial close processes
- Global tax compliance and multi-currency support
- Tight integration with Oracle’s database and Fusion Middleware
Oracle’s strength lies in its robust security framework and deep analytics. It’s a top choice for enterprises prioritizing data governance. Learn more at Oracle ERP Cloud.
3. Microsoft Dynamics 365 – Seamless Integration with Office 365
Microsoft Dynamics 365 combines ERP and CRM capabilities into a unified platform. Its biggest advantage? Native integration with Microsoft 365, Teams, and Azure, making it a favorite among organizations already in the Microsoft ecosystem.
- Unified interface for sales, service, finance, and operations
- AI-driven insights via Power BI and Copilot integration
- Flexible deployment: cloud, on-premise, or hybrid
- Low-code customization with Power Apps
Dynamics 365 is ideal for mid-to-large enterprises looking for a user-friendly, scalable solution. Explore it at Microsoft Dynamics 365.
4. Salesforce – The CRM Powerhouse
While Salesforce started as a CRM, it has evolved into a full-fledged enterprise business software platform with offerings in marketing, service, commerce, and analytics.
- AI-powered Einstein Analytics for predictive insights
- Extensive AppExchange marketplace with 3,000+ integrations
- Customizable workflows with Flow Builder
- Strong mobile and offline capabilities
Salesforce is the go-to choice for customer-centric enterprises. Its cloud-first architecture ensures rapid deployment and scalability. Visit Salesforce.com to learn more.
5. Workday – Modern HR & Financial Management
Workday specializes in human capital management (HCM) and financial management. It’s known for its intuitive interface, real-time analytics, and cloud-native architecture.
- End-to-end HR processes: hiring to retirement
- Workforce planning and talent development tools
- Continuous financial planning and modeling
- Strong mobile experience with AI-driven recommendations
Workday is trusted by Fortune 500 companies like Netflix and Cisco. It’s particularly effective for organizations undergoing digital HR transformation. See Workday’s platform in action.
6. Infor CloudSuite – Industry-Specific Solutions
Infor stands out by offering industry-tailored enterprise business software for sectors like healthcare, manufacturing, and hospitality.
- Built-in AI and analytics with Infor OS (Operating Service)
- Multi-tenant cloud architecture for cost efficiency
- Pre-configured workflows for specific industries
- Integration with IoT and supply chain sensors
Infor’s focus on vertical markets makes it a powerful choice for specialized enterprises. Discover more at Infor.com.
7. NetSuite – Best for Mid-Sized Enterprises
NetSuite, owned by Oracle, is a cloud-based ERP system ideal for growing mid-sized companies. It offers a full suite of applications including financials, CRM, e-commerce, and inventory management.
- Real-time dashboards and financial reporting
- Global business management with multi-subsidiary support
- Scalable architecture for rapid growth
- Strong e-commerce integration with SuiteCommerce
NetSuite is praised for its ease of implementation and quick ROI. It’s a top pick for companies scaling from SMB to enterprise. Learn more at NetSuite’s website.
Benefits of Enterprise Business Software
Investing in enterprise business software is a strategic decision that yields long-term benefits. These systems are not just tools—they are enablers of digital transformation, operational excellence, and competitive advantage.
1. Operational Efficiency & Automation
One of the primary benefits of enterprise business software is the automation of repetitive tasks. From invoice processing to employee onboarding, automation reduces manual errors and frees up staff for higher-value work.
- Automated workflows reduce process cycle times by up to 70%
- AI-driven bots handle routine tasks like data entry and approvals
- Centralized dashboards provide real-time visibility into operations
For example, a manufacturing firm using SAP S/4HANA reported a 45% reduction in order-to-cash cycle time after automation.
2. Enhanced Data Visibility & Decision-Making
Enterprise systems break down data silos by integrating information from across departments. This unified view enables better forecasting, risk management, and strategic planning.
- Real-time KPIs and performance metrics
- Advanced analytics and predictive modeling
- Customizable reports and executive dashboards
A retail chain using Microsoft Dynamics 365 gained a 30% improvement in inventory turnover by leveraging real-time sales and stock data.
3. Scalability & Future-Proofing
As businesses grow, their software must keep pace. Enterprise business software is designed to scale horizontally and vertically, supporting new users, locations, and business models.
- Cloud-based systems allow instant scaling during peak seasons
- Modular architecture enables adding new functionalities (e.g., e-commerce, HR)
- Support for mergers and acquisitions through multi-entity management
This scalability ensures that the software remains relevant for years, protecting the organization’s investment.
Challenges in Implementing Enterprise Business Software
Despite its benefits, implementing enterprise business software is not without challenges. Organizations must navigate technical, cultural, and financial hurdles to ensure success.
1. High Initial Costs & ROI Uncertainty
Enterprise software requires significant investment in licensing, infrastructure, training, and consulting. For some, the return on investment (ROI) may take years to materialize.
- Licensing fees can range from $50,000 to millions, depending on size and scope
- Implementation costs often exceed software costs
- Uncertainty in timeline and business impact can deter decision-makers
However, a 2023 McKinsey study found that companies achieving full adoption of ERP systems saw an average ROI of 182% over five years.
2. Complex Integration & Data Migration
Integrating new software with legacy systems is one of the biggest technical challenges. Data migration must be accurate, secure, and complete to avoid operational disruptions.
- Data cleansing is often required before migration
- API compatibility issues can delay integration
- Downtime during cutover must be minimized
Best practices include phased rollouts, thorough testing, and involving IT and business stakeholders early.
3. Change Management & User Adoption
Even the best software fails if employees resist using it. Change management is critical to ensure smooth adoption.
- Employees may fear job loss or increased workload
- Lack of training leads to underutilization
- Old habits die hard—users may revert to spreadsheets or emails
Solutions include comprehensive training programs, internal champions, and user-friendly interfaces. Salesforce, for instance, offers Trailhead—a gamified learning platform—to boost adoption.
How to Choose the Right Enterprise Business Software
Selecting the right enterprise business software is a strategic process that requires careful evaluation. It’s not just about features—it’s about fit, flexibility, and future readiness.
1. Assess Your Business Needs
Start by identifying your pain points and strategic goals. Are you looking to improve financial reporting? Streamline supply chain operations? Enhance customer service?
- Conduct a gap analysis of current systems
- Engage stakeholders from finance, IT, HR, and operations
- Prioritize must-have vs. nice-to-have features
A retail company might prioritize inventory management and POS integration, while a service firm may focus on project billing and resource planning.
2. Evaluate Vendor Reputation & Support
The vendor’s reliability is as important as the software itself. Look for companies with a proven track record, strong customer support, and a clear product roadmap.
- Check Gartner Magic Quadrant or Forrester Wave reports
- Read customer reviews on platforms like G2 or TrustRadius
- Ask for references and case studies
Vendors like SAP and Oracle have decades of experience, while newer players like Workday are praised for innovation and customer service.
3. Consider Deployment Options: Cloud vs. On-Premise
Today, most enterprise business software is available in cloud, on-premise, or hybrid models. Each has pros and cons.
- Cloud: Faster deployment, lower upfront costs, automatic updates. Ideal for agility and scalability.
- On-Premise: Greater control over data and security. Preferred by highly regulated industries.
- Hybrid: Combines both—useful during digital transformation.
According to IDC, over 70% of new enterprise software deployments in 2024 are cloud-based, reflecting a clear industry trend.
The Role of AI and Automation in Enterprise Software
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and automation are no longer futuristic concepts—they are core components of modern enterprise business software. These technologies are transforming how businesses operate, making systems smarter, faster, and more intuitive.
AI-Powered Insights & Predictive Analytics
AI enables enterprise software to go beyond reporting to prediction. Instead of just showing what happened, it forecasts what will happen.
- Salesforce Einstein predicts customer churn and recommends next-best actions
- Oracle ERP uses AI to detect financial anomalies and prevent fraud
- Workday analyzes workforce trends to suggest retention strategies
These insights allow proactive decision-making, reducing risks and seizing opportunities faster.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA uses software bots to automate rule-based tasks across applications. It’s a game-changer for back-office operations.
- Bots can process invoices, update records, and generate reports 24/7
- Reduces processing time from hours to minutes
- Integrates with ERP and CRM systems without changing underlying code
UiPath and Automation Anywhere are leading RPA platforms that integrate with enterprise business software like SAP and Oracle.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) & Chatbots
NLP allows users to interact with software using natural language. Chatbots and voice assistants are becoming common in HR and customer service.
- Employees can ask, “What’s my PTO balance?” via chatbot
- Managers can request reports using voice commands
- Customers get instant support through AI-powered agents
Microsoft’s Copilot and Salesforce’s Einstein Bot are prime examples of NLP in action.
Future Trends in Enterprise Business Software
The landscape of enterprise business software is evolving rapidly. Emerging technologies and changing business models are shaping the next generation of enterprise tools.
1. Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation combines AI, RPA, machine learning, and process mining to automate entire business processes end-to-end.
- Gartner predicts that by 2026, 60% of enterprises will use hyperautomation platforms
- It enables self-healing workflows and autonomous decision-making
- Reduces human intervention in complex operations
Enterprises adopting hyperautomation report up to 50% reduction in operational costs.
2. Low-Code/No-Code Development
Low-code platforms allow business users to build custom applications without coding. This democratizes software development and speeds up innovation.
- Microsoft Power Apps and Salesforce Lightning enable rapid app creation
- Business analysts can create dashboards, forms, and workflows
- Reduces dependency on IT departments
According to Forrester, low-code platforms will power over 75% of enterprise apps by 2025.
3. Edge Computing & IoT Integration
As more devices connect to enterprise systems, edge computing allows data processing closer to the source—reducing latency and improving real-time decision-making.
- Manufacturers use IoT sensors to monitor equipment health in real time
- Retailers track inventory using smart shelves and RFID tags
- Data is processed locally and synced with central ERP systems
This trend is especially relevant for industries with distributed operations.
What is enterprise business software?
Enterprise business software refers to integrated applications designed to support large organizations in managing core business processes such as finance, HR, supply chain, and customer relations. These systems are scalable, secure, and built for high-volume operations.
What are the main types of enterprise software?
The main types include ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), CRM (Customer Relationship Management), SCM (Supply Chain Management), HRMS (Human Resource Management Systems), and BI (Business Intelligence) tools. Each serves a specific function but often integrates with others for seamless operations.
Is cloud-based enterprise software secure?
Yes, cloud-based enterprise business software is highly secure. Providers like SAP, Oracle, and Microsoft invest heavily in encryption, identity management, and compliance certifications (e.g., ISO 27001, SOC 2). In many cases, cloud solutions are more secure than on-premise systems due to continuous updates and expert monitoring.
How long does it take to implement enterprise software?
Implementation time varies by complexity and scope. Small deployments can take 3–6 months, while large, global rollouts may take 12–24 months. Factors include data migration, customization, integration, and user training.
Can small businesses use enterprise software?
While traditionally for large organizations, many vendors now offer scaled-down versions for mid-sized and growing businesses. NetSuite and Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central are examples of enterprise-grade software accessible to smaller enterprises.
Enterprise business software is a cornerstone of modern business operations. From SAP and Oracle to Salesforce and Workday, the right solution can drive efficiency, innovation, and growth. While implementation poses challenges, the long-term benefits—automation, data visibility, and scalability—make it a worthwhile investment. As AI, cloud computing, and low-code platforms reshape the landscape, enterprises that embrace these technologies will lead the next wave of digital transformation.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: