Enterprise Management System: 7 Powerful Benefits You Can’t Ignore
Ever wondered how big companies manage thousands of tasks, employees, and data every single day? The secret lies in a powerful enterprise management system that ties everything together—smoothly, efficiently, and smartly.
What Is an Enterprise Management System?

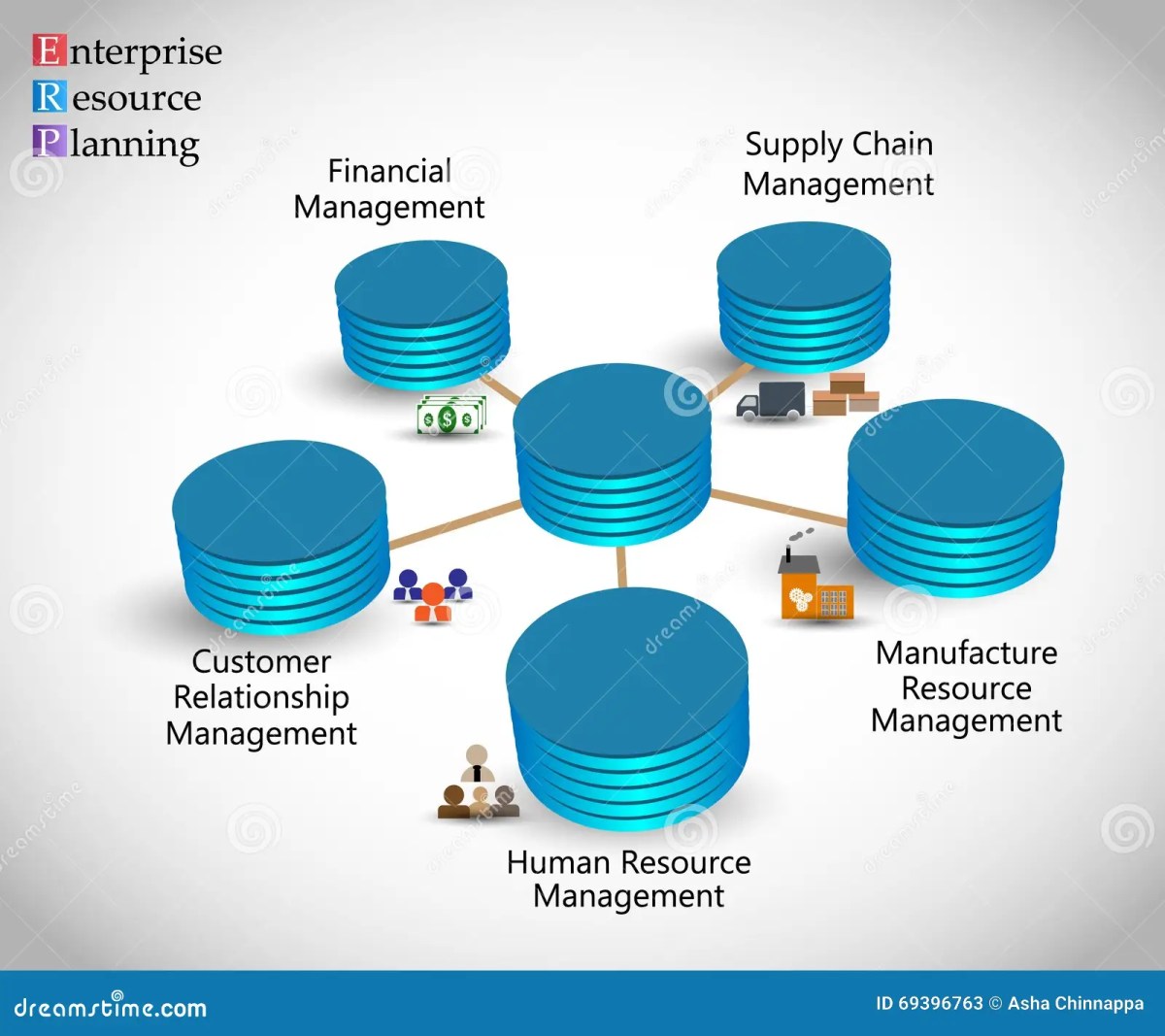
An enterprise management system (EMS) is a comprehensive software platform designed to integrate and manage all core business processes across an organization. From finance and human resources to supply chain and customer relations, an EMS acts as the central nervous system of a modern enterprise.
Core Definition and Scope
The term ‘enterprise management system’ refers to a suite of integrated applications that help organizations plan, execute, monitor, and optimize their operations. Unlike standalone tools, an EMS connects departments, breaks down data silos, and ensures real-time visibility across the business.
- It consolidates data from various departments into a single source of truth.
- It supports decision-making with analytics and reporting tools.
- It scales with business growth, making it ideal for mid-sized to large organizations.
Evolution of Enterprise Management Systems
The concept of enterprise-wide management systems began in the 1960s with Material Requirements Planning (MRP) systems used in manufacturing. Over time, these evolved into Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II), and eventually into Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems in the 1990s.
Today’s enterprise management system goes beyond ERP, incorporating cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and advanced automation. According to Gartner, modern EMS platforms are now more agile, modular, and user-centric than ever before.
“The future of enterprise management is not just integration—it’s intelligence.” — Gartner Research, 2023
Key Components of an Enterprise Management System
A robust enterprise management system isn’t a single tool but a collection of interconnected modules, each serving a specific business function. These components work together to ensure seamless data flow and operational harmony.
Financial Management Module
This module handles all financial operations, including general ledger, accounts payable and receivable, budgeting, and financial reporting. It ensures compliance with accounting standards and provides real-time insights into the company’s financial health.
- Automates invoice processing and payment tracking.
- Generates balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow reports.
- Integrates with tax compliance tools for global operations.
Human Capital Management (HCM)
Also known as HR management, this component manages employee data, payroll, recruitment, performance reviews, and training. Modern HCM systems within an enterprise management system often include AI-driven analytics for workforce planning.
For example, platforms like Oracle HCM Cloud offer predictive analytics to identify turnover risks and skill gaps.
- Centralizes employee records and onboarding workflows.
- Supports remote work with self-service portals.
- Tracks KPIs related to employee engagement and productivity.
Supply Chain and Inventory Management
This module oversees procurement, inventory control, order fulfillment, and logistics. It ensures that products are available when needed while minimizing excess stock.
With real-time tracking and demand forecasting, companies can reduce lead times and improve supplier relationships. SAP’s supply chain solutions, for instance, use machine learning to predict disruptions before they occur (SAP).
- Enables just-in-time inventory strategies.
- Integrates with third-party logistics providers.
- Provides end-to-end visibility from raw materials to delivery.
Top Benefits of Implementing an Enterprise Management System
Deploying an enterprise management system is not just a technological upgrade—it’s a strategic transformation. Organizations that adopt these systems report significant improvements in efficiency, transparency, and scalability.
Improved Operational Efficiency
By automating repetitive tasks and streamlining workflows, an EMS eliminates bottlenecks and reduces manual errors. For example, instead of relying on spreadsheets and email chains, purchase orders can be auto-generated based on inventory levels.
- Reduces process cycle times by up to 50% in some industries.
- Minimizes redundant data entry across departments.
- Enables faster approvals through digital workflows.
Real-Time Data and Business Intelligence
One of the most powerful advantages of an enterprise management system is access to real-time dashboards and analytics. Decision-makers can view sales trends, inventory status, or employee performance at a glance.
Microsoft Dynamics 365, for example, integrates Power BI to deliver interactive reports that update in real time (Microsoft). This empowers leaders to act quickly and confidently.
- Supports predictive analytics for sales and demand forecasting.
- Offers customizable KPIs for different departments.
- Facilitates scenario modeling for strategic planning.
Enhanced Collaboration Across Departments
When finance, sales, HR, and operations all use the same system, collaboration becomes seamless. There’s no more waiting for reports or chasing down approvals.
A shared database means that when a sales team closes a deal, the finance team sees it instantly, and the warehouse knows to prepare shipment. This level of synchronization is only possible with a fully integrated enterprise management system.
- Breaks down departmental silos.
- Improves interdepartmental communication.
- Reduces misalignment between teams.
Types of Enterprise Management Systems
Not all enterprise management systems are created equal. Depending on the business needs, size, and industry, organizations can choose from several types of EMS platforms.
On-Premise Enterprise Management Systems
These systems are installed and run on the company’s own servers and infrastructure. They offer full control over data and customization but require significant upfront investment and IT resources.
- Ideal for large enterprises with strict data security requirements.
- Higher total cost of ownership (TCO) due to hardware and maintenance.
- Longer implementation timelines compared to cloud solutions.
Cloud-Based Enterprise Management Systems
Hosted on remote servers and accessed via the internet, cloud-based EMS platforms are becoming the standard. They offer faster deployment, lower costs, and automatic updates.
According to a 2023 IDC report, over 70% of new EMS deployments are now cloud-first or cloud-only.
- Scalable: Easily add users or modules as needed.
- Accessible from anywhere, supporting hybrid work models.
- Includes built-in disaster recovery and backup features.
Hybrid Enterprise Management Systems
Some organizations opt for a hybrid model, combining on-premise and cloud components. This approach allows them to keep sensitive data in-house while leveraging the flexibility of the cloud for other functions.
- Offers a transitional path for legacy system migration.
- Provides flexibility in data governance and compliance.
- Can be more complex to manage due to integration challenges.
How to Choose the Right Enterprise Management System
Selecting the right enterprise management system is a critical decision that can impact your business for years. It requires careful evaluation of your current processes, future goals, and technical capabilities.
Assess Your Business Needs
Start by identifying the key pain points in your organization. Are you struggling with inventory accuracy? Is financial reporting delayed? Do departments operate in silos?
Conduct interviews with stakeholders from each department to gather requirements. This will help you prioritize which modules and features are essential.
- Create a list of must-have vs. nice-to-have features.
- Map current workflows to identify inefficiencies.
- Define success metrics for the EMS implementation.
Evaluate Vendor Options
There are dozens of EMS vendors in the market, each with different strengths. Some of the leading players include SAP, Oracle, Microsoft, Infor, and Workday.
When evaluating vendors, consider:
- Industry-specific functionality (e.g., manufacturing, retail, healthcare).
- User experience and ease of adoption.
- Integration capabilities with existing software.
- Vendor reputation, customer support, and update frequency.
Request demos and trial versions to test usability firsthand.
Consider Scalability and Future-Proofing
Your business will grow, and your enterprise management system should grow with it. Choose a platform that supports modular expansion and adapts to new technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain.
Ask vendors about their roadmap for innovation. Are they investing in machine learning? Do they support mobile access and offline functionality?
- Ensure the system can handle increased data volume and user load.
- Check for API availability for future integrations.
- Look for platforms with open architecture and developer communities.
Common Challenges in Enterprise Management System Implementation
Despite their benefits, implementing an enterprise management system is not without challenges. Many organizations face obstacles that can delay timelines, increase costs, or reduce user adoption.
Data Migration Issues
Transferring data from legacy systems to a new EMS is often complex. Incomplete, duplicate, or inconsistent data can lead to errors in the new system.
To mitigate this, conduct a thorough data audit before migration. Cleanse and standardize data, and validate it after transfer.
- Use ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tools for efficient migration.
- Perform test migrations in a sandbox environment.
- Assign a data steward to oversee quality control.
Employee Resistance and Training Gaps
Change is hard. Employees accustomed to old processes may resist adopting a new enterprise management system. Lack of proper training exacerbates this issue.
A successful rollout requires a change management strategy. Communicate the benefits clearly, involve users early, and provide comprehensive training programs.
- Offer role-based training sessions.
- Create user guides and video tutorials.
- Appoint internal champions to support peers.
Integration with Existing Systems
Most companies already use CRM, email, or specialized software. Ensuring the EMS integrates smoothly with these tools is crucial.
Use middleware or API gateways to connect disparate systems. Prioritize integrations that deliver the highest ROI, such as linking EMS with CRM or e-commerce platforms.
- Test integrations in a staging environment first.
- Monitor API performance and error logs regularly.
- Choose EMS platforms with pre-built connectors for common tools.
Future Trends Shaping Enterprise Management Systems
The world of enterprise management is evolving rapidly. Emerging technologies are transforming how EMS platforms function and deliver value.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s embedded in modern enterprise management systems. From chatbots that handle HR queries to algorithms that optimize supply chains, AI enhances decision-making and automation.
For example, IBM’s Watson integrates with EMS platforms to provide natural language processing for customer service and predictive maintenance for equipment.
- Enables intelligent forecasting and anomaly detection.
- Automates routine tasks like invoice matching and approvals.
- Improves personalization in customer and employee experiences.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
IoT devices generate vast amounts of real-time data—from factory sensors to delivery trucks. Integrating this data into an enterprise management system allows for proactive monitoring and optimization.
In manufacturing, IoT-enabled EMS can detect machine failures before they happen, reducing downtime. In logistics, real-time GPS tracking improves delivery accuracy.
- Connects physical assets to digital systems.
- Supports predictive maintenance and energy management.
- Enhances traceability in regulated industries like pharmaceuticals.
Blockchain for Transparency and Security
Blockchain technology is being explored for secure transaction logging within enterprise management systems. It ensures data integrity and auditability, especially in supply chain and finance.
Walmart, for instance, uses blockchain via IBM Food Trust to track food origin and safety in its supply chain—an integration that could be part of a broader EMS (IBM Food Trust).
- Prevents tampering with financial and inventory records.
- Enables smart contracts for automated payments.
- Builds trust with partners and regulators.
Real-World Examples of Enterprise Management System Success
Theoretical benefits are great, but real-world results speak louder. Let’s look at how leading companies have leveraged enterprise management systems to transform their operations.
Nestlé: Global ERP Transformation
Nestlé embarked on a massive EMS initiative called ‘One Nestlé’ to standardize processes across 190 countries. By implementing SAP ERP globally, they achieved:
- 30% reduction in IT costs.
- Unified financial reporting across regions.
- Faster month-end closing from weeks to days.
The project took over a decade but resulted in a more agile and transparent organization.
Unilever: Digital Supply Chain Integration
Unilever integrated its enterprise management system with AI and IoT to create a responsive supply chain. The system predicts demand fluctuations and adjusts production accordingly.
- Reduced stockouts by 20%.
- Improved forecast accuracy by 35%.
- Enhanced sustainability by minimizing waste.
This digital transformation was powered by a cloud-based EMS platform with advanced analytics.
Maersk: Blockchain-Enabled Logistics
Maersk, the world’s largest container shipping company, partnered with IBM to develop TradeLens, a blockchain-based platform integrated into their enterprise management system.
- Reduced documentation processing time by 40%.
- Increased transparency across ports and customs.
- Enabled real-time shipment tracking for customers.
This innovation redefined how global trade data is managed and shared.
What is an enterprise management system?
An enterprise management system (EMS) is an integrated software platform that manages core business processes such as finance, HR, supply chain, and operations across an entire organization. It centralizes data and streamlines workflows to improve efficiency and decision-making.
What are the main benefits of an EMS?
The key benefits include improved operational efficiency, real-time data access, better interdepartmental collaboration, scalability, and enhanced compliance. Modern EMS platforms also offer advanced analytics and automation capabilities.
How long does it take to implement an enterprise management system?
Implementation time varies based on complexity, ranging from 3-6 months for small businesses using cloud systems to 1-3 years for large enterprises with custom on-premise solutions.
Is cloud-based EMS secure?
Yes, reputable cloud-based enterprise management systems use advanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits. In many cases, they are more secure than on-premise systems due to dedicated cybersecurity teams and automatic updates.
Can an EMS integrate with other business tools?
Absolutely. Modern EMS platforms offer robust APIs and pre-built connectors to integrate with CRM, e-commerce, payroll, and other third-party applications, ensuring seamless data flow across systems.
Adopting an enterprise management system is more than a tech upgrade—it’s a strategic move toward agility, insight, and long-term growth. From streamlining daily operations to enabling AI-driven decisions, the right EMS can transform how a business operates. While challenges like data migration and user adoption exist, the rewards far outweigh the risks. As technology evolves, so too will enterprise management systems, bringing smarter, faster, and more connected enterprises. The future belongs to those who integrate, automate, and innovate.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: